Automated guided vehicles, also known as AGVs, have become a critical part of modern logistics and manufacturing. In factories, warehouses, and distribution centers across the world, AGVs are taking over tasks that once required constant human involvement. These machines help businesses move materials efficiently, safely, and with minimal downtime.
This article will walk you through what an AGV is, how it operates, and why so many companies today are investing in these intelligent solutions.
What is an AGV?
An AGV is a self-operating vehicle built to transport goods without needing a human operator. The key difference between AGV vs AMR (Autonomous Mobile Robots) lies in how they move and adapt. AGVs require predefined guidance, whereas AMRs can make real-time navigation decisions using onboard sensors and mapping systems.
You will find AGVs carrying pallets, moving raw materials, or delivering components across production floors, all while sticking to precise paths or adjusting to real-time changes.
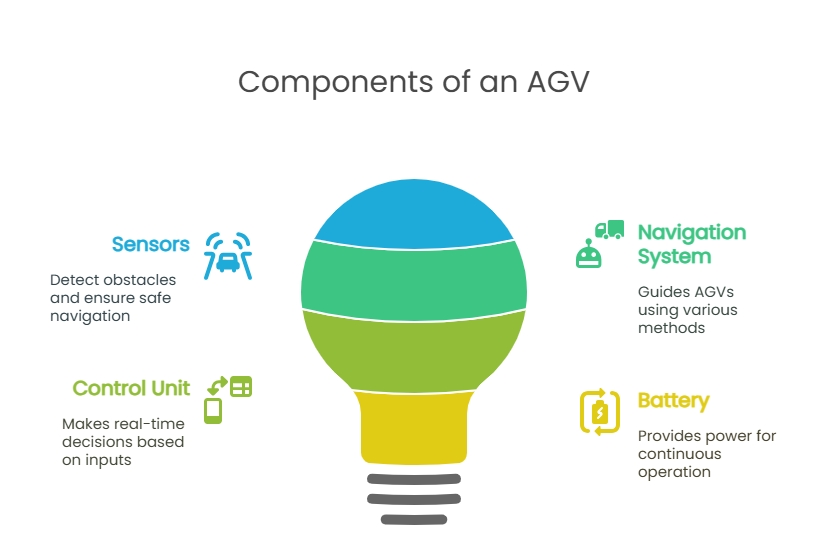
In order to know what is an AGV completely, you need to understand the different parts of these machines. These parts include:
- Sensors: They help the AGV detect obstacles, stay aware of its surroundings, and ensure safe navigation.
- Navigation system: Different types of systems guide AGVs, ranging from simple floor markers to advanced scanning technologies.
- Control unit:These units act like the AGV’s brain, making real-time decisions based on sensor inputs and task instructions.
- Battery:AGVs typically use lithium-ion batteries for fast charging and long life, ideal for continuous use. Lead-acid batteries are a lower-cost option but require longer charging and more maintenance.
How Do AGVs Work?
There are different types of automatic guided vehicles, so their working differs a bit from each other. But the foundation of these vehicles remains the same.
Depending on the environment and the level of complexity required, AGVs use one or more navigation technologies:
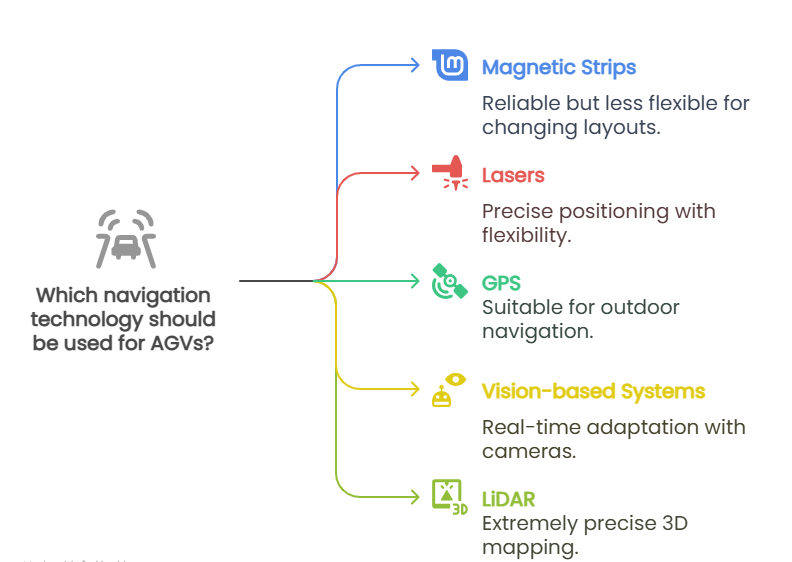
- Magnetic strips: These strips are laid on the floor and guide the AGV along set routes. They are reliable, though less flexible for changing layouts.
- Lasers:By reflecting laser beams off targets placed around the facility, the AGV can calculate its exact position and navigate freely.
- GPS (Global Positioning System):Particularly useful outdoors, GPS enables AGVs to find their way across large spaces, although they are less effective inside buildings.
- Vision-based systems (cameras): With onboard cameras, AGVs can interpret their surroundings and adapt in real-time, giving them greater flexibility.
- LiDAR (Light Detection and Ranging): This technology scans the environment with laser light to create detailed 3D maps, offering extremely precise positioning.
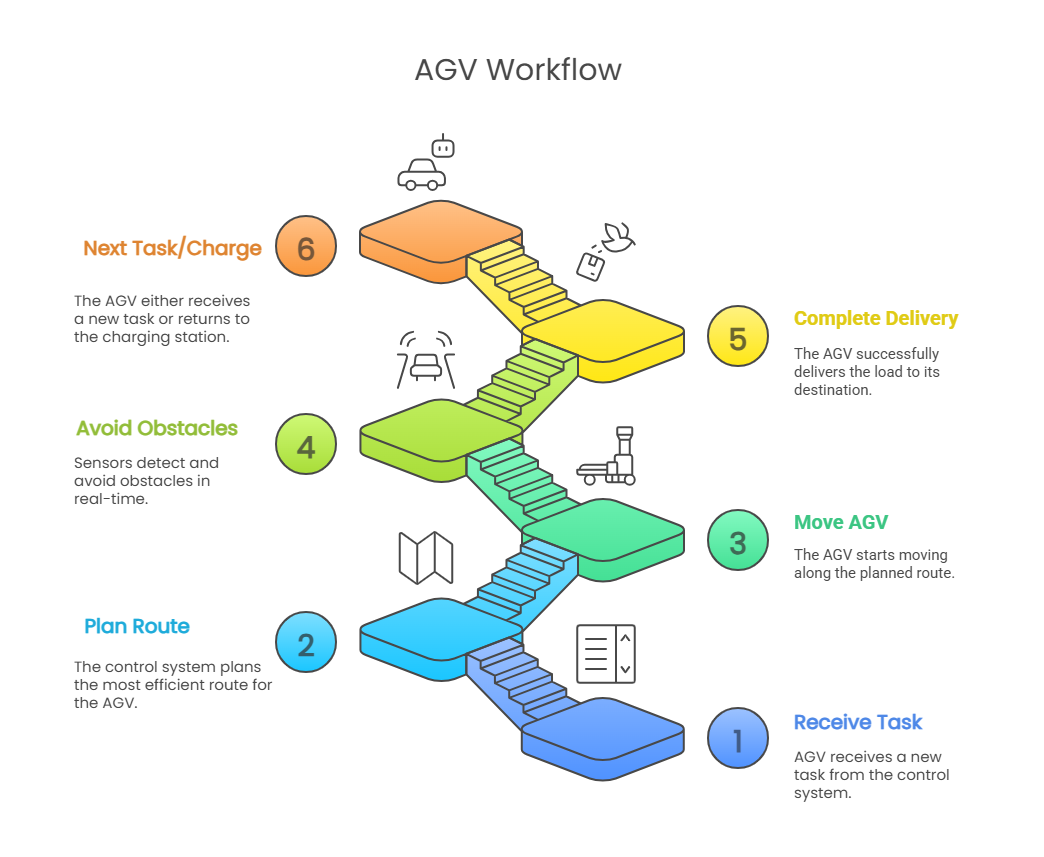
The typical AGV workflow begins when it receives a task, like picking up a load from a staging area. Its control system quickly plans the best route and sets the AGV in motion. As it moves, sensors constantly scan for obstacles and make real-time adjustments to avoid any collisions. Meanwhile, the navigation system ensures the AGV stays on course until the delivery is complete. Once the task is done, the AGV either heads to its next assignment or returns to a charging station if needed.
Key Benefits of AGVs
AGVs offer a wide range of strategic benefits that go beyond simple automation, driving measurable improvements:
- Increased operational efficiency:AGVs maintain a steady workflow without needing breaks or supervision, which leads to faster production cycles.
- Reduced labor costs: By taking over repetitive transport tasks, AGVs free up human workers for more skilled roles while reducing staffing expenses.
- Enhanced safety and reduce workplace accidents: Built-in collision avoidance and emergency-stop functions dramatically lower the risk of injuries.
- 24/7 operation with minimal downtime: As long as there is battery power, AGVs can keep working day and night with minimal downtime.
When these advantages are added up, it becomes clear why AGVs are often among the first steps companies take when moving toward smart factory setups.
Common Applications of Automated Guided Vehicles
While AGVs originally found their place in heavy industry, their use today spans a wide range of sectors, such as:
- Manufacturing: Moving parts and supplies across assembly lines with perfect timing.
- Warehousing and distribution:Shuttling products from storage to shipping areas in fast-paced fulfillment centers.
- Automotive: Handling heavy engine blocks and other car parts safely through different production stages.
- Food and beverage: Assisting in the quick, clean, and safe transport of products where hygiene standards are strict.
- E-commerce and retail:Meeting tight delivery windows by automating picking and packing tasks in busy distribution hubs.
Every industry leverages AGVs a little differently, but the end goal remains the same: faster, safer, and more reliable operations.

AGV Solutions from HELI
Anhui Heli, a globally recognized leader in material handling and forklift equipment, offers a robust lineup of automated guided vehicles designed to meet the evolving needs of businesses across industries.
Among HELI’s standout offerings are two highly efficient models that combine advanced technology with practical design: the 3.5t i-Series Counterbalanced AGV and the 1.5-1.6t i-Series Fork Over Stacker AGV.
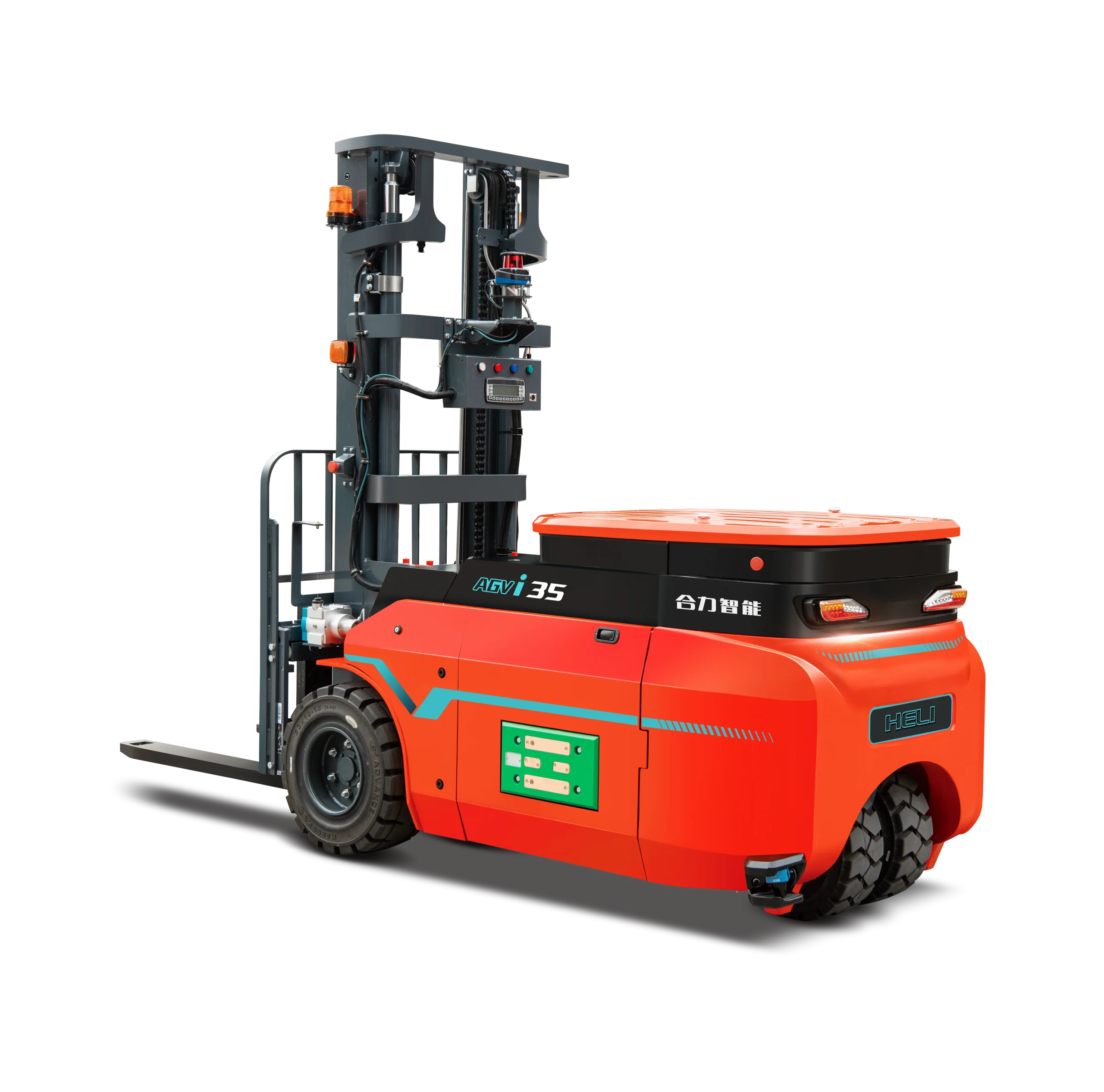
3.5t i-Series Counterbalanced AGV
The 3.5t i-Series Counterbalanced AGV is built for heavy-duty material transfers both indoors and outdoors, offering a load capacity of up to 3.5 tons without reduction at a 3-meter lift.
It has a small turning radius (1920 mm) and front-wheel dual drive for strong maneuverability even in tighter spaces. Powered by a large-capacity lithium-ion battery, it delivers longer run times and includes a side-placed automatic charging system with an integrated charger for faster recharging.
Equipped with laser navigation and 5G/Wi-Fi communication, it achieves a maximum speed of 5 km/h and a lifting height of up to 5,500 mm, making it a powerful and flexible solution for demanding operations.

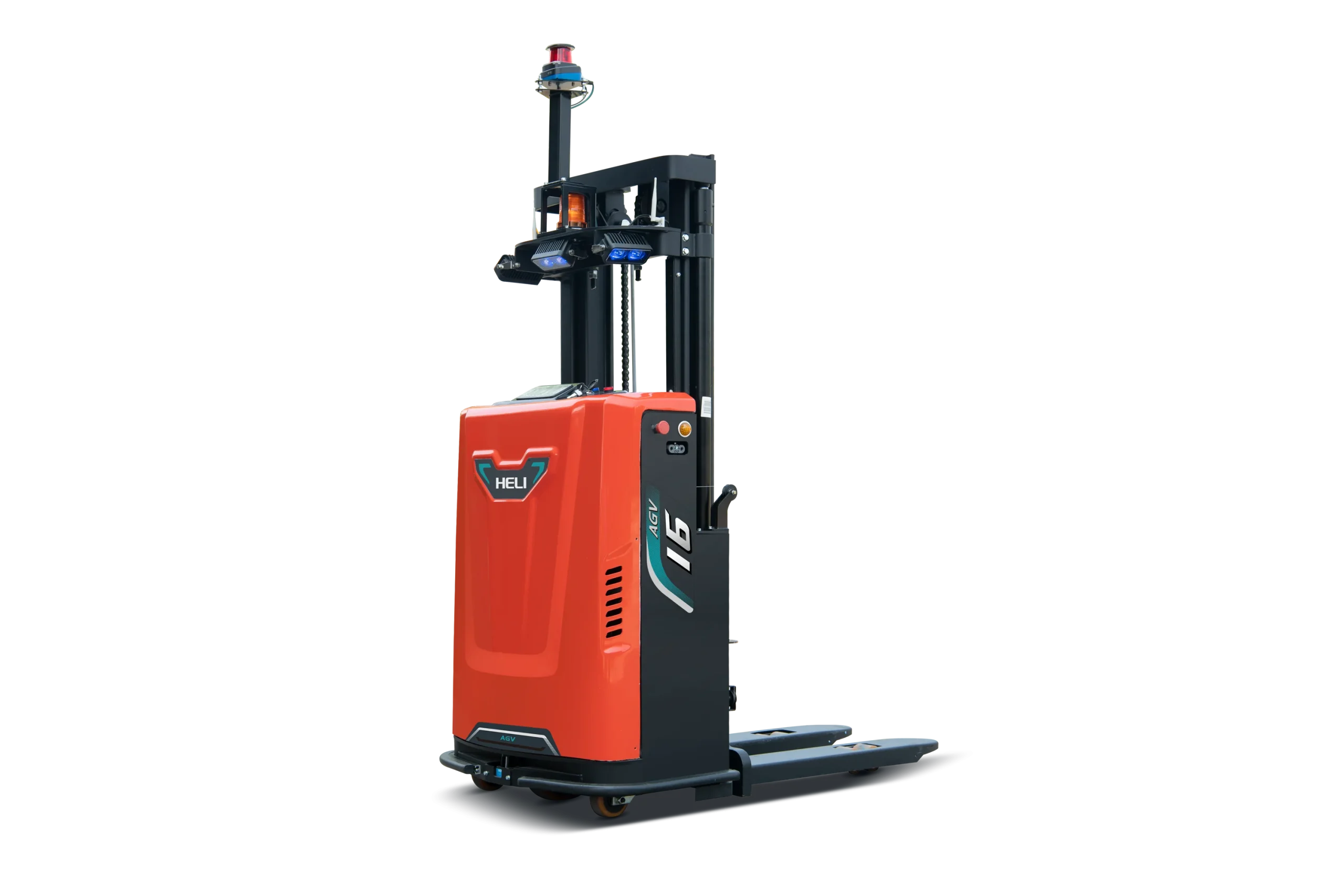
1.5-1.6t i-Series Fork Over Stacker AGV
The 1.5-1.6t i-Series Fork Over Stacker AGV is designed for material handling within warehouses and production lines.
It supports up to 1.6 tons of load without reduction at 3 meters, features a compact structure for minimal aisle space usage, and is powered by a maintenance-free AC steering motor.
With side-placed automatic charging, integrated laser navigation, and 5G/Wi-Fi connectivity, it ensures reliable performance and easy system integration.

Wrapping-Up
AGVs are revolutionizing industries by automating material movement, slashing labor costs, and minimizing workplace risks—helping businesses stay competitive with 24/7 operations.
As automation becomes critical for staying competitive, investing in proven AGV solutions is a smart move. HELI’s AGV lineup offers reliable, high-performance options for businesses ready to optimize their logistics and manufacturing operations. Reach out now to explore tailored AGV solutions that fit your business needs.

